Understanding the Importance of Sensors in Cannabis Cultivation
Cannabis plants have specific environmental requirements for optimal growth and development. Temperature, humidity, light intensity, and CO2 levels need to be carefully monitored and controlled to create high yields consistently. Sensors give growers the real-time data they need to create, and more importantly, maintain these ideal conditions for their plants.
Beyond helping maintain optimal growth conditions, sensors also contribute to ensuring plant health. By monitoring various environmental parameters, growers can detect and limit the impact from issues like nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, or diseases, and take action to address them.
The Role of Sensors in Optimizing Growth Conditions
Sensors are invaluable tools for achieving the perfect balance of temperature, humidity, light, and CO2 in the cultivation environment. They continuously measure these parameters and provide growers with accurate data that can be used to fine-tune the grow room conditions.
Temperature sensors help maintain the optimal temperature range for cannabis plants, ensuring that they are neither too hot nor too cold. Humidity sensors, on the other hand, allow growers to closely monitor and control moisture levels, preventing issues like mold or fungal growth.
Light intensity sensors play a critical role in ensuring that cannabis plants receive the right amount of light for photosynthesis. By measuring the intensity of light hitting the plants, growers can adjust the distance between the plants and the grow lights to optimize exposure.
CO2 sensors help growers maintain optimal CO2 levels in the grow room (critical!). Higher CO2 concentrations can significantly enhance photosynthesis and overall plant growth, while inadequate levels can lead to stunted growth and reduced yields. Sensor data allows growers to fine-tune CO2 supplementation for maximum benefit (and higher yields).
Furthermore, sensors can also monitor other factors such as pH levels in the nutrient solution, which is crucial for nutrient uptake by the plants. By ensuring the pH is within the optimal range, growers can prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that can negatively impact plant health and growth.
Finally, sensors can also measure the electrical conductivity (EC) of the nutrient solution, providing growers with information about the concentration of dissolved salts. This allows them to adjust the nutrient solution accordingly, ensuring that the plants receive the right balance of essential minerals.
Ensuring Plant Health with Accurate Sensor Data
Accurate sensor data is crucial for identifying any potential issues affecting plant health. And is also one of the biggest issues with sensors that aren’t specific to cannabis. By continuously monitoring various environmental parameters, growers can detect deviations from optimal conditions and take timely action to rectify them.
For example, if a sensor detects elevated humidity levels in the grow room, it could indicate the presence of excessive moisture or poor ventilation. This information enables growers to implement corrective measures such as improving airflow or adjusting dehumidification systems to prevent the development of mold or mildew.
If a light intensity sensor indicates insufficient light reaching the plants, growers can adjust the positioning of the lights or consider adding supplemental lighting to ensure proper growth and development.
Sensors can also help detect pest infestations at an early stage. This is done through temperature and humidity sensors (mostly). They can detect changes in the environment that may attract pests or create favorable conditions for their reproduction. By receiving real-time data from the sensors, growers can promptly implement pest control measures to prevent the infestation from spreading and causing damage to the plants.
Sensors play a crucial role in cannabis cultivation by providing growers with real-time data on various environmental parameters that will make sure plant health is optimal, and more importantly if it isn’t, give growers real time data to make changes. By harnessing the power of sensors, cannabis growers can maximize yields, improve quality, and ensure the success of their cultivation operations.
Types of Sensors Used in Cannabis Cultivation
Several types of sensors are commonly utilized in cannabis cultivation to monitor and control the growth environment. Let’s explore some of the most essential ones:
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
Temperature and humidity sensors are fundamental in maintaining optimal conditions for cannabis plants. They provide growers with accurate data on temperature and humidity levels, allowing them to adjust environmental controls accordingly. These sensors help ensure that the grow room remains within the ideal temperature range and that humidity levels are suitable for robust plant growth.
Temperature sensors are designed to measure the ambient temperature in the grow room. They can be placed at different locations within the space to provide a comprehensive understanding of temperature fluctuations. This information is crucial for growers to make informed decisions about adjusting heating or cooling systems to maintain the desired temperature range.
Humidity sensors, on the other hand, measure the amount of moisture present in the air. They help growers monitor the humidity levels and prevent issues such as mold or mildew growth. By keeping the humidity within the optimal range, growers can create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth and minimizes the risk of diseases.
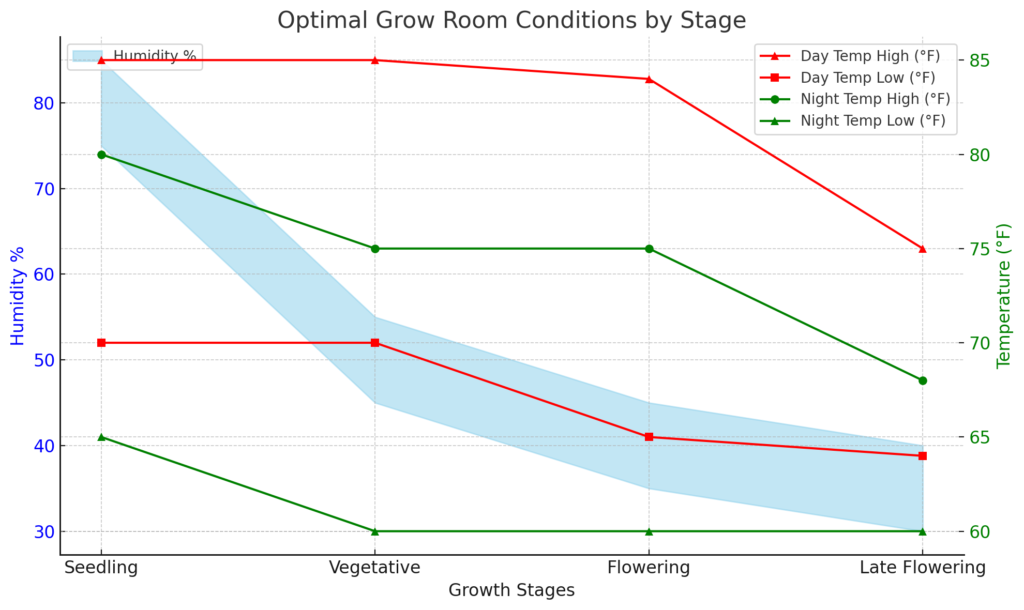
VPD and and Sensors in Cannabis Cultivation
Before diving into how VPD charts and sensors work together, let’s break down what Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) is and why it’s a game-changer in growing cannabis and in growing in general.
What is Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)?
Vapor Pressure Deficit, or VPD, is a crucial concept in horticulture, especially in controlled environments like cannabis grows. It’s a way to understand the relationship between temperature and humidity in the air around your plants. Simply put, VPD measures the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and the maximum amount it can hold at a certain temperature. This difference is key because it influences how plants take in water and nutrients through their leaves.
VPD plays a vital role in plant health and growth. Here’s why it’s important:
Transpiration Control: VPD affects how much water vapor plants release into the air. The right VPD level ensures that plants transpire effectively, which is crucial for nutrient uptake and overall health.
Disease Prevention: Too much humidity can lead to fungal diseases, while too little can stress the plants. VPD helps in maintaining optimal humidity levels, reducing the risk of disease.
Growth Optimization: By managing VPD, growers can create an environment that promotes faster growth and better yields.
The Connection Between VPD and Sensors
Understanding VPD is one thing, but keeping it at the optimal level is where sensors come in. Sensors provide the data needed to monitor and adjust the growing environment, ensuring that the VPD stays in the ideal range for cannabis plants. This is where the real magic happens in a controlled grow environment.
Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors are vital for monitoring the water content in the growing medium. They help prevent over or under watering by providing real-time data on soil moisture levels. This allows growers to optimize irrigation schedules, ensuring that the plants receive adequate water without drowning the root system or causing water stress.
These sensors are typically inserted into the soil and measure the moisture content at different depths. This information helps growers determine when and how much water to provide to the plants. By maintaining optimal soil moisture levels, growers can promote healthy root development and prevent issues such as root rot.
It’s important to note that soil sensors alone aren’t going to give you all the data you need by themselves. They don’t replace physically assessing the plants. Often looking at the leaves can help greatly: Look for yellowing leaves (over, or under-watering plants), Limp leaves (over-watering), or brittle or brown leaves (severe under-watering). Physically touching the soil with a “finger test” is also a very easy way to see how dry or wet a plant is. If the soil is dry past your second knuckle, it may call for a watering.
Light Intensity Sensors
Light intensity sensors are used to measure the amount of light hitting the plants. They are mission critical to help optimize the distance between the plants and the grow lights, ensuring that plants receive the right amount of light for optimal photosynthesis at each stage of growth. By understanding and fine-tuning light intensity, growers can achieve maximum yield and quality much more consistently.
Lighting sensors are typically placed at different heights within the grow room to capture variations in light intensity. They provide growers with data on the amount of light reaching the plants, allowing them to adjust the positioning of the grow lights . This helps prevent issues such as light burn or insufficient light, which can and will negatively impact plant growth and overall yield.
CO2 Sensors
CO2 sensors are crucial for maintaining appropriate CO2 levels in the cultivation environment. They measure the concentration of CO2 and provide growers with real-time data. This information helps optimize CO2 supplementation, enhancing plant growth and overall yields.
CO2 sensors are typically placed in strategic locations within the grow room to capture accurate readings. By maintaining optimal CO2 levels, growers can enhance photosynthesis, boost plant growth, and increase the overall yield of their cannabis crops.
VPD and and Sensors
Before diving into how VPD charts and sensors work together, let’s break down what Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) is and why it’s a game-changer in growing cannabis and in growing in general.
What is Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)?
Vapor Pressure Deficit, or VPD, is a crucial concept in horticulture, especially in controlled environments like cannabis grows. It’s a way to understand the relationship between temperature and humidity in the air around your plants. Simply put, VPD measures the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and the maximum amount it can hold at a certain temperature. This difference is key because it influences how plants take in water and nutrients through their leaves.
VPD plays a vital role in plant health and growth. Here’s why it’s important:
Transpiration Control: VPD affects how much water vapor plants release into the air. The right VPD level ensures that plants transpire effectively, which is crucial for nutrient uptake and overall health.
Disease Prevention: Too much humidity can lead to fungal diseases, while too little can stress the plants. VPD helps in maintaining optimal humidity levels, reducing the risk of disease.
Growth Optimization: By managing VPD, growers can create an environment that promotes faster growth and better yields.
The Connection Between VPD and Sensors
Understanding VPD is critical in a commercial cannabis cultivation, but keeping it at the optimal level is even more important, and where sensors come in. Sensors provide the data needed to monitor and adjust the growing environment, ensuring that the VPD stays in the ideal range for cannabis plants.
Choosing the Right Sensors for Your Cannabis Grow
When selecting sensors for your cannabis cultivation operation, several factors need to be considered:I hav
Factors to Consider When Selecting Sensors
- Accuracy: Choose sensors that provide precise and reliable data for optimal decision-making. This is the most important factor in choosing a sensor.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the sensors you choose are compatible with your existing environmental control systems so you can understand how the cultivation is operating as a whole, and not in a segmented multi-application format.
- Durability: Select sensors that are designed to withstand the specific conditions of cannabis cultivation, such as high humidity or temperature fluctuations.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the sensors and their long-term benefits in terms of improved yields and efficiency. You do get what you pay for, so make sure you commit resources to avoid getting whitelabeled or non-cannabis specific hardware.
Understanding Sensor Specifications
Before making a purchase, it is essential to understand the specifications of the sensors you are considering. Look for information on accuracy, range, response time, and any additional features that may be relevant to your specific needs.
Installing and Positioning Your Sensors
Proper installation and positioning of sensors are critical for obtaining accurate and reliable data. Follow these best practices:
Best Practices for Sensor Installation
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for sensor installation to ensure proper functioning.
- Ensure that sensors are securely placed in the designated positions.
- Regularly inspect and maintain sensors to prevent any issues that may affect their performance.
Optimal Sensor Placement for Accurate Readings
The positioning of sensors can significantly impact the accuracy of the data they provide. Consider the following guidelines:
- Temperature and humidity sensors should be placed at canopy level, where the plants are most sensitive to environmental conditions.
- Soil moisture sensors should be strategically inserted into the growing medium, ensuring accurate readings from the root zone.
- Light intensity sensors should be positioned at the same height as the canopy, capturing the amount of light received by the plants accurately.
- CO2 sensors should be placed near areas where CO2 supplementation is provided, ensuring an accurate representation of the overall CO2 concentration.
Interpreting Sensor Data for Cannabis Cultivation
Collecting sensor data is just the first step. The key lies in interpreting the data to make informed cultivation decisions. Here’s how:
Decoding Sensor Readings
Regularly analyze the sensor readings and look for any deviations from the optimal ranges. These deviations could indicate issues that need attention. For example, temperature readings that are consistently too high might indicate a problem with cooling or ventilation.
It is essential to keep a record of the sensor data over time, as trends can provide valuable insights. By comparing current readings with historical data, patterns can be identified, and proactive adjustments can be made to optimize growth conditions.
Making Adjustments Based on Sensor Data
Based on the interpretation of the sensor data, make necessary adjustments to fine-tune the cultivation environment. For example, if light intensity readings are consistently low, consider adjusting the positioning of the grow lights or adding supplemental lighting to improve light exposure.
Regular monitoring and adjustment based on sensor data will enable growers to maintain optimal growth conditions throughout the cultivation cycle, resulting in healthier plants and higher yields.
Sensors , PlanaCan, and higher yields
In cannabis cultivation, it’s not just the gathering of data from sensors for soil moisture, lighting, CO2, and Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) that’s crucial, but also how growers react to this information. Timely and appropriate responses to sensor data are the key to boosting plant health, yield, and quality. This is where cultivation management platforms like PlanaCan become vital. When something goes wrong, being able to understand who is working that day, which harvest needs help, bridge the gap between the issue, and resolving it.